


Next: Eigenfunctions and Eigenvalues
Up: Operators
Previous: Basic Properties of Operators
Contents
Almost all operators encountered in quantum mechanics are linear
operators. A linear operator is an operator which satisfies the following
two conditions:
where 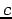 is a constant and
is a constant and 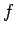 and
and 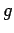 are functions.
As an example, consider the operators
are functions.
As an example, consider the operators 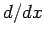 and
and 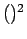 .
We can see that
.
We can see that 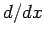 is a linear operator because
is a linear operator because
However, 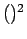 is not a linear operator because
is not a linear operator because
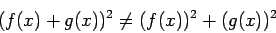 |
(47) |
The only other category of operators relevant to quantum mechanics is the
set of antilinear operators, for which
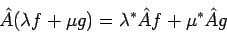 |
(48) |
Time-reversal operators are antilinear (cf. Merzbacher
[2], section 16-11).



Next: Eigenfunctions and Eigenvalues
Up: Operators
Previous: Basic Properties of Operators
Contents
David Sherrill
2006-08-15